ArXiv Paper Title:
QuAILoRA: Quantization-Aware Initialization for LoRA
October 22, 2024
Keywords:
Quantization, LoRA, LLMs, Memory Efficiency
Read the paper on ArXiv
Enhancing QLoRA: QuAILoRA's Quantization-Aware Initialization
Fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) is computationally expensive. Quantized Low-Rank Adaptation (QLoRA) offers a clever solution by quantizing the base model, significantly reducing memory usage. However, this quantization introduces errors that can hurt the model's performance. This is where QuAILoRA steps in! This research introduces a novel quantization-aware initialization method for QLoRA, designed to minimize these pesky quantization errors right from the start.
QuAILoRA cleverly tackles the performance drop caused by QLoRA's quantization. It does this by carefully initializing the LoRA matrices (A and B). The goal? To keep the activations (or weights) of the QLoRA model as close as possible to a full-precision base model during initialization.
The method uses a two-step process:
- Uncalibrated Initialization: QuAILoRA begins by using Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) to initialize A and B, minimizing an uncalibrated quantization objective. Think of this as a rough first draft.
- Calibrated Refinement: Next, it iteratively refines these initializations using a calibrated quantization objective function. This refinement ensures the QLoRA model's behavior closely matches the full-precision model, especially on a chosen calibration dataset. This is where the magic happens, fine-tuning the initial draft for optimal performance.
This entire process is computationally inexpensive, requiring only the solution of small linear systems.
Experimental Results: Across LLMs and Tasks
The researchers put QuAILoRA to the test across various LLMs (LLaMA, OPT, BLOOM, Pythia), model sizes, and downstream tasks. The results are impressive:
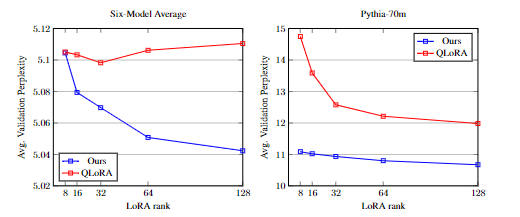
- Consistent Improvement: QuAILoRA consistently improves validation perplexity compared to standard QLoRA initialization.
- Significant Gains with Low-bit Quantization: The benefits are even more pronounced when using lower-bit quantization (e.g., 4-bit), significantly reducing memory footprint. In fact, QuAILoRA with 4-bit QLoRA models achieved about 75% of the performance improvement seen in 8-bit QLoRA models!
- Robustness to Calibration Dataset: The method is remarkably robust to the choice of calibration dataset.
- Enhanced LoRA Rank Performance: Increasing the LoRA rank further boosted QuAILoRA's performance, unlike the baseline QLoRA.
- No Impact on Convergence Speed: QuAILoRA didn't significantly affect the fine-tuning convergence speed.
QuAILoRA offers a practical and effective way to enhance QLoRA's performance without increasing memory usage during fine-tuning. It consistently boosts performance across a variety of LLMs and tasks, particularly where quantization errors are more significant. This makes it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners looking to efficiently fine-tune LLMs.
While QuAILoRA shows great promise, there's plenty of room for further exploration:
- Scaling to Larger Models: Testing QuAILoRA on even larger LLMs (beyond 30B parameters) could uncover further insights.
- Lower Bit-depth Quantization: Exploring extremely low-bit quantization (e.g., 1-bit, 2-bit) could lead to even greater memory efficiency.
- Adaptive Calibration Strategies: Dynamically adjusting the calibration dataset during fine-tuning could further optimize performance.
- Extending to Other PEFT Methods: The core concepts of QuAILoRA could be beneficial for other parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods.
QuAILoRA represents a significant step towards more efficient and effective fine-tuning of LLMs. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it a promising technique for future research and applications.

