
This post dives into a recent research paper that challenges conventional wisdom about Visual Language Models (VLMs) and Large Language Models (LLMs) in image classification. Get ready to rethink your approach to combining these powerful tools!
The research paper, "Rethinking VLMs and LLMs for Image Classification," explores the effectiveness of combining VLMs and LLMs for image classification tasks. The researchers ran extensive experiments across seven models, ten datasets, and numerous prompt variations. Their results revealed some surprising findings:
VLMs often beat VLM+LLM combos for basic tasks: Contrary to popular belief, VLMs without LLMs often outperformed VLM+LLM combinations when it came to basic object and scene recognition. This suggests that adding an LLM isn't always a performance boost for simpler image classification tasks.
LLMs shine with reasoning and external knowledge: However, the story changes when the task involves reasoning and requires external knowledge. In these more complex scenarios, VLM+LLMs demonstrated a significant performance advantage over VLMs alone.
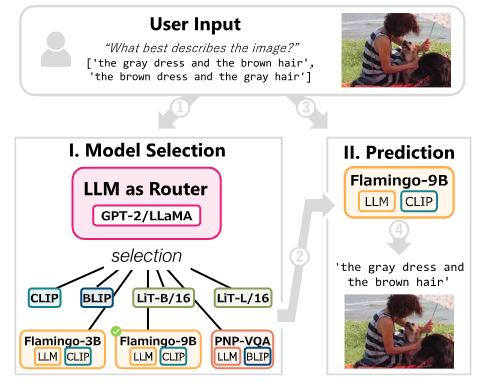
To harness the strengths of both VLMs and LLMs efficiently, the researchers developed a lightweight "LLM router." This small LLM acts as a task manager, intelligently deciding which model (VLM or VLM+LLM) is best suited for a given image classification task. The results are impressive:
State-of-the-art accuracy: The LLM router matched or surpassed the performance of heavyweight methods like GPT-4V and HuggingGPT.
Improved cost-effectiveness: This smart routing approach significantly reduces the computational cost compared to running multiple models for every task.
While the LLM router shows promising results, the researchers also identified some areas for future exploration:
Generalizability: More research is needed to confirm the router's effectiveness across a wider range of tasks and datasets.
Data quality matters: The router's performance is directly linked to the quality of its training data. Addressing biases and inaccuracies in the training data is crucial.
Sophisticated routing strategies: Exploring more advanced routing methods, like ensemble approaches or hierarchical routing, could further enhance performance.
Multimodal inputs: Incorporating additional data types, beyond text and image metadata, could improve the router's decision-making capabilities.
This research highlights that a more strategic approach to integrating VLMs and LLMs is needed. Instead of always combining them directly, a system that intelligently chooses the best model for the task at hand can yield superior results with improved efficiency. The LLM router offers a compelling example of this smarter approach, promising exciting possibilities for the future of image classification and beyond.