ArXiv Paper Title:
S4ST: A Strong, Self-transferable, faSt, and Simple Scale Transformation for Transferable Targeted Attack
October 21, 2024
Keywords:
Adversarial Attacks, Deep Neural Networks, Transferable Attacks, Image Transformations
Read the paper on ArXiv
Boosting Targeted Attacks: The SST Transformation
Transferable targeted adversarial attacks (TTAs) against deep neural networks (DNNs) are significantly more challenging than untargeted attacks. Current solutions either demand extensive extra data and training or severely overfit to the surrogate model. This paper introduces a novel transformation method, Strong, Self-transferable, fast, and Simple Scale Transformation (SST), designed to overcome these limitations and significantly improve TTAs. Instead of focusing solely on loss functions, SST emphasizes the often-overlooked role of image transformations in gradient calculations. Let's dive in!
SST is built on several key insights:
- Image transformations are crucial: Simple TTAs struggle with the gradient vanishing problem. Image transformations are key to mitigating this and enhancing transferability.
- Self-transferability predicts black-box transferability: How well adversarial perturbations transfer to different transformations of the same image (self-transferability) is a strong indicator of their black-box transferability.
- Simple scaling is surprisingly effective: A scaling-centered strategy proves exceptionally effective at improving targeted transferability, outperforming many complex transformations.
Using these insights, SST incorporates:
- Modified scaling transformations
- Complementary transformations
- Block-wise scaling
This multifaceted approach results in a highly efficient and effective TTA method.
Key Findings and Results
Extensive experiments on the ImageNet-Compatible dataset demonstrated SST's superiority:
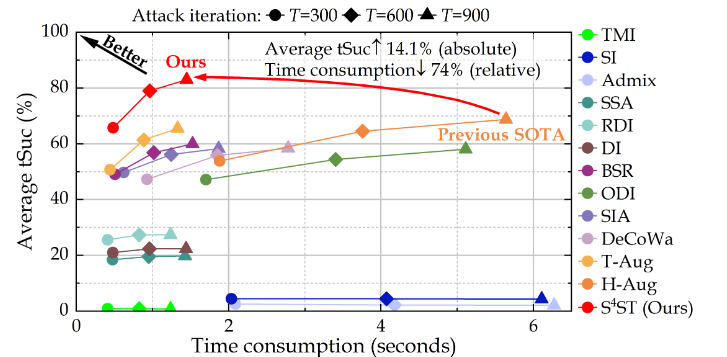
- State-of-the-art (SOTA) performance: SST achieved SOTA average targeted transfer success rates, outperforming the previous leading method by over 14%.
- Significant efficiency gains: SST required only 25.7% of the execution time compared to the previous SOTA method.
- Real-world effectiveness: SST demonstrated effectiveness against real-world APIs.
These results validate the hypotheses and demonstrate SST's significant advancement in the field.
Limitations and Future Directions
While SST shows great promise, it's important to acknowledge some limitations:
- The study used a diverse but not exhaustive set of black-box models. Further research should explore generalizability to other DNN architectures and defense mechanisms.
- The findings are based on the ImageNet-Compatible dataset. Generalizability to other datasets requires further investigation.
- SST's performance depends on the choice of surrogate model. More research is needed to assess the impact of different surrogate models.
Future research could explore:
- Other types of image transformations.
- More robust blind estimators for black-box transferability prediction.
- Applications of SST to other security-critical domains (autonomous driving, medical image analysis, etc.).
- Development of robust defense mechanisms against TTAs, informed by the insights gained from this research.
SST represents a significant leap forward in transferable targeted adversarial attacks. It provides a highly efficient and effective method for generating transferable targeted adversarial examples, surpassing existing methods in both effectiveness and efficiency. The research underscores the critical role of image transformations and offers valuable insights for designing and evaluating future transformation strategies. This work highlights the realistic threats posed by TTAs and paves the way for more robust defense mechanisms.

